Understanding PVC Material: The Backbone of Modern Manufacturing
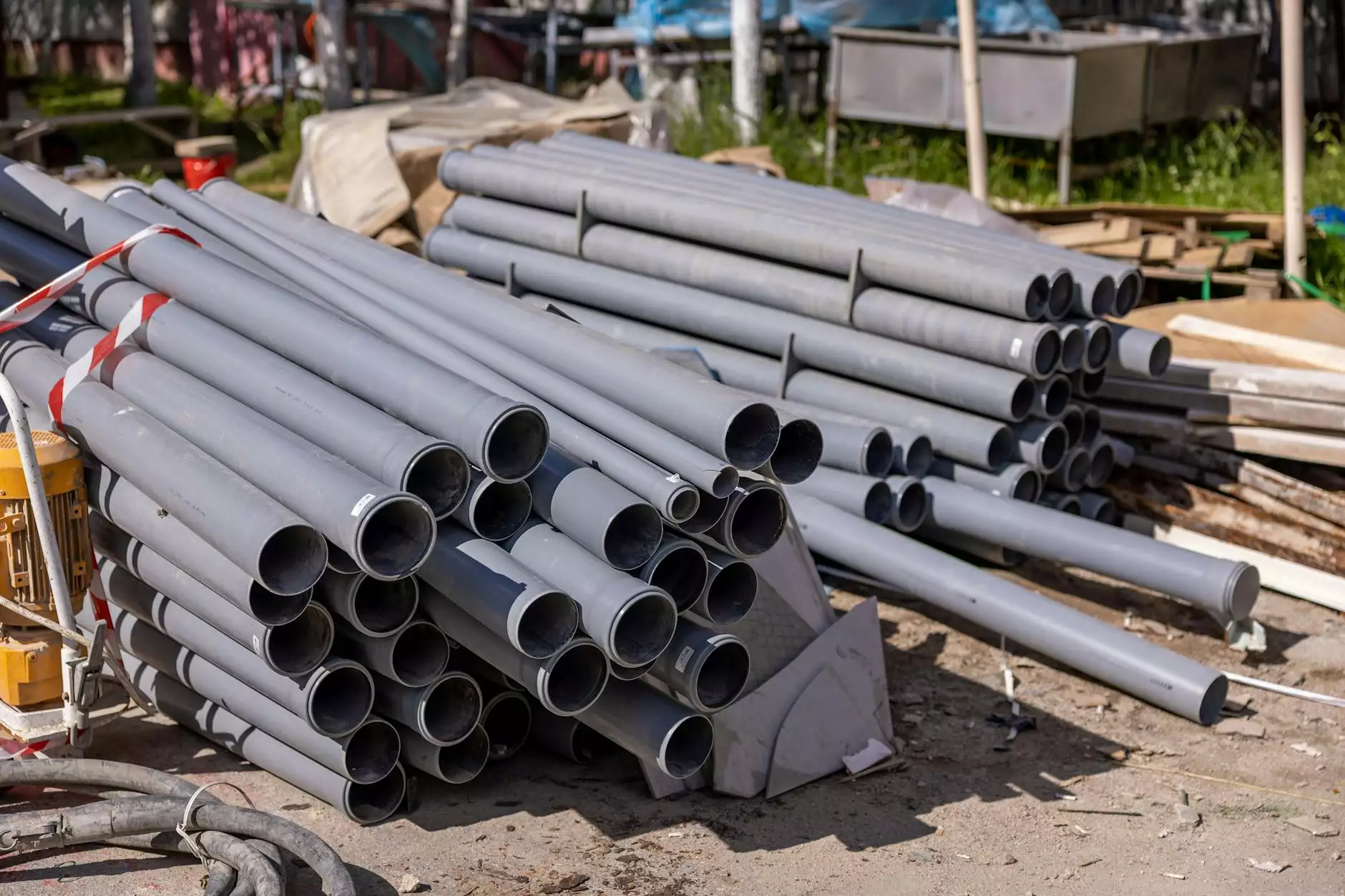

PVC, or Polyvinyl Chloride, is one of the most widely used synthetic plastic polymers globally. In this article, we will delve deep into the characteristics, applications, and benefits of pvc material, highlighting its significance in various industries such as construction, manufacturing, and more. Whether you are a manufacturer, architect, or consumer, understanding PVC can provide you with insights into its advantages, potential, and future in the market.
What is PVC Material?
PVC material is a synthetic polymer made from the polymerization of vinyl chloride. It is a versatile plastic known for its durability, chemical resistance, and low-cost production. PVC can be produced in flexible and rigid forms, making it suitable for a myriad of applications.
The Composition of PVC
The chemical structure of PVC gives it unique properties. It consists of:
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Provides stability during processing.
- Stabilisers: Denotes added compounds that enhance UV resistance and thermal stability.
- Plasticizers: Make PVC flexible; used in soft PVC products.
Key Properties of PVC Material
PVC material possesses numerous properties that make it an attractive option for various applications:
- Durability: PVC is extremely resilient and can withstand wear and tear. It is also resistant to water, chemicals, and corrosion.
- Lightweight: Compared to traditional materials like wood and metal, PVC is much lighter, reducing transportation costs and making it easier to handle.
- Cost-effective: The production process for PVC is generally low-cost, allowing for affordability in manufacturing products.
- Versatility: PVC can be manufactured in both flexible and rigid forms, making it applicable in a wide range of products and industries.
- Recyclability: PVC is recyclable, making it an eco-friendly option when proper recycling practices are followed.
Applications of PVC Material
The applications of pvc material are extensive and span across various sectors. Here are some major applications:
Construction Industry
PVC is predominantly used in the construction industry due to its durability and weather resistance. Common applications include:
- Pipes and Fittings: PVC pipes are widely used for drainage, sewage, and irrigation systems due to their corrosion resistance.
- Windows and Doors: PVC frames offer excellent insulation properties and require minimal maintenance.
- Roofing Membranes: PVC roofing is durable and resistant to harmful UV rays, making it ideal for flat roof applications.
Manufacturing Industry
Within the manufacturing sector, pvc material is utilized in a variety of products:
- Packaging: Many packaging materials like bottles, containers, and shrink wraps utilize PVC for its durability and flexibility.
- Automotive Parts: PVC is used in automotive interiors, exterior trim, and dashboards due to its lightweight properties and resistance to degradation.
- Medical Devices: Flexible PVC is used to manufacture blood bags and tubes, essential in medical containers and equipment.
Consumer Products
PVC is also prevalent in everyday consumer items:
- Toys: Many toys are produced from PVC due to its versatility and safety when properly formulated.
- Footwear: PVC is used in the production of sandals and other shoes due to its water resistance and comfort.
- Flooring: Vinyl flooring is made from PVC and offers a wide range of styles at a fraction of the cost of traditional materials.
The Advantages of Using PVC Material
Choosing pvc material offers several benefits, particularly for manufacturers and businesses:
1. Cost Efficiency
Using PVC in manufacturing processes can significantly reduce costs. Its low raw material cost and easy processing methods result in lower production expenses, which can be a critical factor for businesses aiming for profitability.
2. Environmental Impact
PVC is often criticized for its environmental footprint; however, with advancements in recycling technologies, the lifecycle of PVC can be effectively managed. Many products made from PVC can be recycled into new products, contributing to a circular economy.
3. Safety
When produced and used correctly, PVC is considered safe for various applications. Its non-toxic formulation is often utilized in medical applications, ensuring safety in sensitive environments.
The Future of PVC Material
The future of pvc material in business appears promising as industries continue to innovate. Here are some key trends shaping its future:
1. Sustainable Innovations
Sustainability is at the forefront of many manufacturing processes today. The PVC industry is exploring new formulations and recycling processes to minimize its environmental impact.
2. Expanding Applications
With the advancement of technology, the applications of PVC are continually expanding. Innovative uses in 3D printing, electronics, and advanced composites are gaining traction.
3. Regulatory Developments
As regulations regarding plastic materials evolve, companies will need to adapt. Understanding compliance and adopting best practices in PVC production will be crucial for future success.
Conclusion
PVC material has firmly established itself as a vital component in various industries due to its unique properties and versatile applications. From construction to consumer goods, its influence is profound and widespread. As we move forward, the emphasis on sustainability and innovative applications will ensure that PVC continues to play an important role in manufacturing and product development.
If you’re in the business of manufacturing or using products made from PVC, it’s essential to stay informed about the latest trends and advancements in the industry. By embracing the versatility and benefits of PVC, businesses can thrive in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
For more information about PVC products and manufacturing, visit hidroplasto.ro.